Transfer Pricing
[Based on the Public Consultation Document released by the Ministry of Finance, UAE on 28 April 2022.]
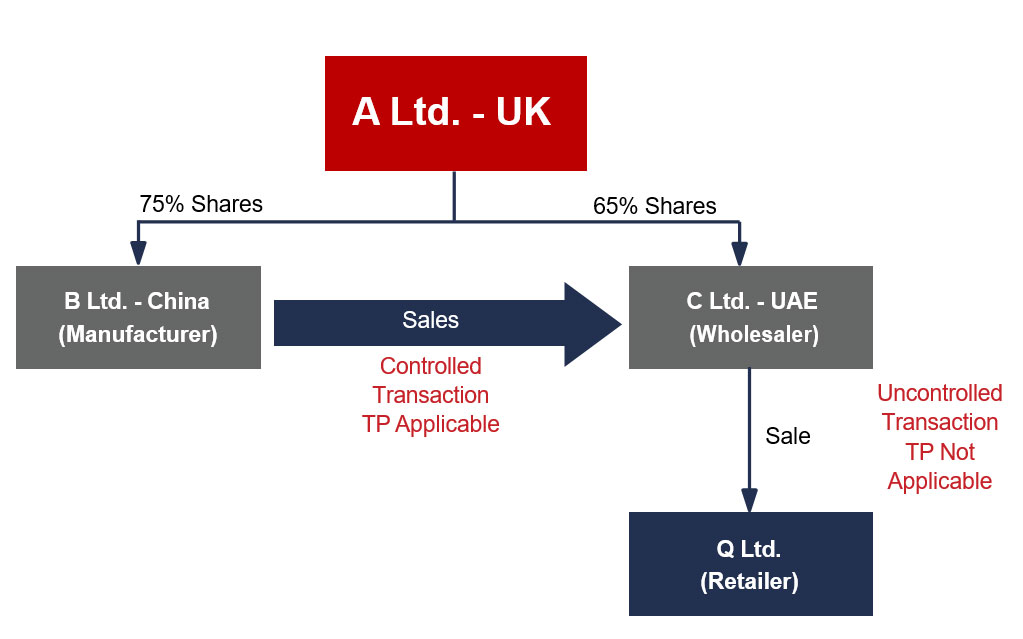
Transfer Pricing refers to the rules and methods for pricing transactions within and between enterprises under common ownership or control. The UAE Corporate Tax regime will have Transfer Pricing rules to ensure that the price of a transaction is not influenced by the relationship between the parties involved.
In order to achieve this outcome, the UAE will apply the internationally recognized “arm’s length” principle to transactions and arrangements between related parties and with connected persons.
Related Parties
A related party is an individual or entity who has a pre-existing relationship with a business that is within the scope of the UAE Corporate Tax regime through ownership, control, or kinship (in the case of natural persons).
The following will be considered as Related Parties for the purpose of UAE Corporate Tax:
| 1 | Two or more individuals | Related to the fourth degree of kinship or affiliation, including by birth, marriage, adoption, or guardianship |
| 2 | An individual and a legal entity | Individuals alone or together with a related party directly or indirectly own a 50% or greater share in or control the legal entity |
| 3 | Two or more legal entities |
|
| 4 | Taxpayer | Its branch or permanent establishment |
| 5 | Unincorporated partnership | All partners |
| 6 | Exempt and non-exempt business | Activities of the same person |
Connected Persons
Payments or benefits provided by a business to its “Connected Persons” will be deductible only if the business can demonstrate that the payment or benefit:
- corresponds with the market value of the service provided; and
- is incurred wholly and exclusively for the purposes of the taxpayer’s business.
A person will be considered as ‘connected’ to a business that is within the scope of the
UAE Corporate Tax regime under the following circumstances:
| 1 | Individual, who has direct or indirect ownership/control in the taxable person |
| 2 | Director / Officer of the taxable person |
| 3 | An individual related to the owner, director, or officer |
| 4 | Any other partner of the unincorporated partnership |
| 5 | A related party of any of the above |
Arm’s length principle
All Related Party transactions and transactions with Connected Persons will need to comply with transfer pricing rules and the arm’s length principle as set out in the OECD Transfer
OECD Guidelines - Transfer Pricing Methods
The latest OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines (released in 2022) recommend five widely used methods of establishing transfer pricing. They are:
| 1 | The Comparable Uncontrolled Price (CUP) Method | The CUP method compares transactions made between related and unrelated organizations. By comparing the price of goods and services in an intercompany transaction with the price used by independent parties, a benchmark price can be determined. |
| 2 | The Cost-Plus Method (CPM): | The cost plus method begins with the costs incurred by the supplier of the goods /services and then an appropriate cost plus mark-up is added to make an appropriate profit in light of the functions performed and market conditions. Once the mark-up is determined, it should be equal to what a third party would make for a comparable transaction, in a comparable context with similar external market conditions. |
| 3 | The Resale Price Method (RPM): | The resale price method begins with the price at which a product that has been purchased from an Associated Enterprise is resold to an independent enterprise. This resale price is then reduced by an appropriate gross margin representing the amount out of which the reseller would seek to cover its selling and other operating expenses. This method is commonly used by resellers and distributors, as opposed to manufacturers. |
| 4 | Transactional Net Margin Method (TNMM): | TNMM is based on the net profit of a controlled transaction, rather than comparable external market pricing. The net profit is then compared with independent enterprises net profit. |
| 5 | Transactional Profit Split Method(TPSM): | TPSM is a method that identifies the relevant profits to be split for associated enterprises from a controlled transaction and then splits those profits between the associated enterprises on an economically valid basis that approximates the division of profits that would have been agreed upon at arm’s length. |
Over and above the aforementioned methods of arriving at arm’s length price, the new OECD Guidance Note also includes guidance on specific transactions like:
- Hard to Value Intangibles – BEPS Action Plan 8
- Financial Transactions - Risks and Capital Transactions – BEPS Action Plan 9
- High-Risk Transactions - controlled transactions that are not commercially rational (e.g. management fee, HO expenses, etc.) – BEPS Action Plan 10
- Business Restructurings
Transfer Pricing documentation requirements
Businesses will have to maintain appropriate documentation in respect of transactions with Related Parties and Connected Persons as specified under OECD BEPS Action 13, including:-
- Master File; and
- Local files
where arm’s length value of their related party transactions exceeds a certain threshold.
Our comments:
It is indicated that the scope of Transfer Pricing will include not only foreign transactions but also domestic transactions, subject to a threshold limit.
It will become essential for the businesses to maintain and demonstrate that every transaction (above threshold) is being conducted at arm’s length. Transfer Pricing benchmarking test / study would be required to be conducted in case of transaction covered under this provision.
Further, payment to connected persons has also been brought under this regulation, which ensures a check on payment made to senior management, partners etc.